There are several parasites that can inhabit human skin. For the first time such worms were found in India, but now they are found in other latitudes. Parasites under the skin cause a person a lot of discomfort and require treatment. They are not as dangerous as worms in other organs, but with a long course of the disease they can lead to serious complications. In our article we will list all types of subcutaneous parasites, the symptoms of the diseases they cause.
Varieties of subcutaneous parasites and methods of infection
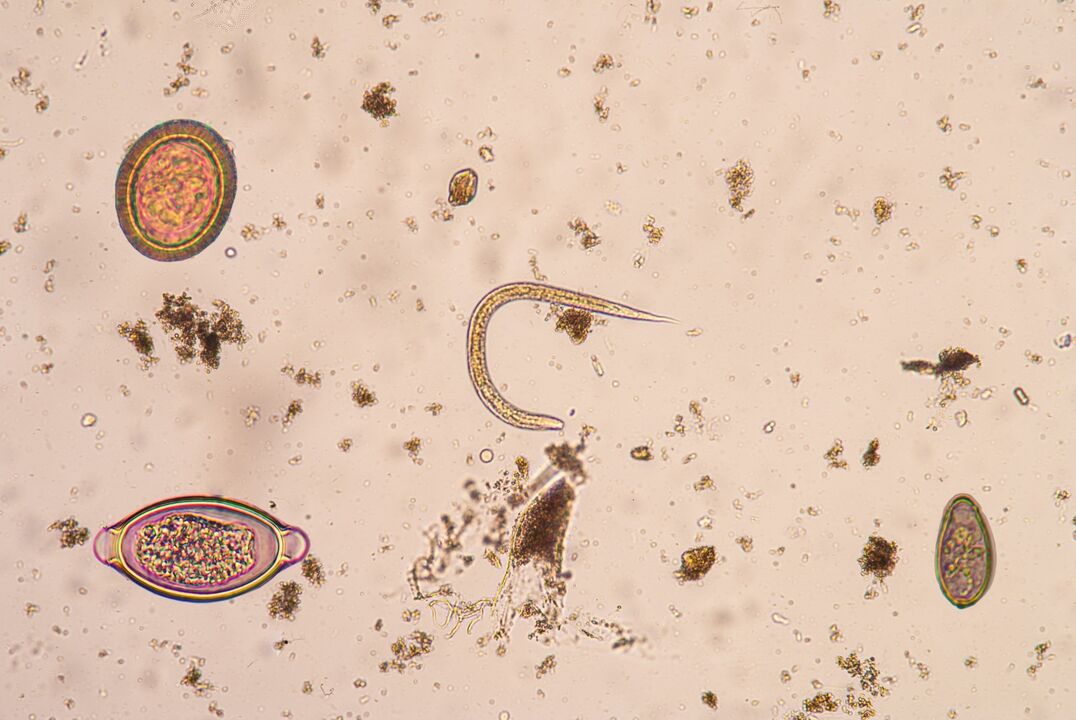
If you want to know who is crawling under the skin, the following subcutaneous parasites are found in people:
- Heartworm disease. This disturbance causes the larval stage of the nematode. Infection occurs when a mosquito (louse, flea or tick) bites, which is a carrier of the disease. A sexually mature individual reaches a length of 30 cm, and the larva of this parasite is microscopic. After infection, it develops under a person's skin for 3 months. Domestic dogs and cats can also transmit the infection.
- If we list which parasites live under the skin, we cannot fail to mention the heartworms. Infection is caused by some types of roundworms. In this case, various diseases arise: onchocerciasis, dipetalonematosis, loiasis and mansonellosis. The carriers of worms and their intermediate hosts are insects (mosquitoes, midges, horseflies, etc. ). They infect human heartworms with larvae, as a result of which worms appear in the skin.
- Another skin parasite in humans is cysticercus larvae. They cause cysticercosis. Invasion occurs through the intestines, where the worms enter with dirty hands, water or food. The cysticercus is an oval vesicle containing the parasite's scolex inside. Subcutaneous worms can change from round to spindle-shaped. Man acts as an intermediate teacher.
- Schistosomiasis is a disease caused by worms in a person of the order of flukes. These are worms up to 2 cm long. The larvae of this parasite, which can swim in water, are cercariae. They can enter the human body directly through the skin. This infection can live in any organ, even under the skin.
- Rishta is another worm under the skin. These white worms cause dracunculiasis and are classified as large roundworms. Their intermediate hosts are aquatic copepods. First, the parasite enters the human stomach, then from the retroperitoneal space it enters the skin. Males reach a length of 10 cm, and females - 120 cm.
Symptoms of heartworm disease

The larvae of this parasite with the bloodstream can spread throughout the body and lodge in the eyes, pulmonary artery, heart, serous cavities, perirenal adipose tissue and under the skin. If there is an invasion by a type of worm called Dirofilaria repens, the conjunctiva or subcutaneous fat is affected.
The signs and symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- painful seals appear at the site of the insect bite;
- within a couple of days in one third of patients, a displacement of the seal of 20-30 cm from the site of the bite occurs;
- a person may feel distension, burning, and itching at the site of the bite;
- there is a feeling of crawling and wriggling under the skin;
- periods of remission are followed by episodes of exacerbation;
- the subcutaneous worm provokes the appearance of abscesses and bubbles (a worm lives inside them in the connecting capsule);
- sometimes the abscesses open on their own and white parasites crawl out of the skin.
If the conjunctiva is damaged, the following symptoms are present:
- swelling, itching and tearing;
- a feeling that a foreign body is present in the eye or eyelid;
- a person cannot fully open the eyelid;
- vision deteriorates;
- a worm can be seen under the conjunctiva;
- a lump is visible under the skin of the eyelid;
- the person has a crawling sensation under the skin or in the eyes;
- if the parasite enters the eyeball, diplopia and swelling of the eye appear.
Important! Heartworm disease is accompanied by neurosis, fears and insomnia. In addition, the patient develops irritability, headache, general weakness and other signs.
Symptoms of filariasis
After invasion, filariasis can develop over a period of several years. Various symptoms and signs can develop depending on the form of the disease. Common to these parasitic diseases will be the appearance of ulcers and rashes, damage to the eyes and lymph nodes, fever, the development of elephantiasis of the scrotum and limbs, as these are muscle parasites.
Onchocerciasis
With onchocerciasis, parasites in human muscles are manifested by the following symptoms:
- itchy skin;
- feverish condition;
- weakness;
- dryness and peeling of the skin;
- skin hyperpigmentation (genitals, legs, axillary and inguinal folds);
- papular rash;
- erysipelas;
- papules can form long-lasting ulcers;
- under the skin, worms cause atrophy of hair follicles, sweat glands and epidermis;
- painful fibrous knots form under the skin;
- with eye damage, glaucoma, iridocyclitis, conjunctivitis, corneal cyst, keratitis and other eye diseases develop.
Dipetalonematosis
These subcutaneous worms in humans cause the following symptoms:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- erythematous or maculopapular rash;
- dizziness;
- fever;
- swelling of the lower limbs, face and genitals;
- articolar pains;
- pain in the heart;
- symptoms of meningoencephalitis.
Loiasis
Parasites living under the human skin, with loiasis, contribute to the appearance of the following clinical picture of the disease:
- skin rashes;
- feverish condition;
- parasites in human muscles can cause muscle abscesses;
- pain in the limbs;
- swelling of the skin in limited areas, which does not go away for a long time;
- if parasites get into the eye, blepharitis or conjunctivitis develops;
- disturbance of urination with localization of infection in the urethra.
Important! These subcutaneous parasites in humans can lead to complications in the form of meningitis, heart failure, encephalitis.
Mansonellosis
With this form of the disease, worms under the human skin can provoke the following symptom complex:
- itchy skin rashes;
- articolar pains;
- feverish condition;
- swelling of the skin;
- dropsy of the testicle;
- numbness of the limbs;
- an increase in inguinal lymph nodes.
Symptoms of cysticercosis
These parasites on human skin can easily penetrate with food into the digestive tract, where the embryo's membrane dissolves and the larva emerges. They enter the bloodstream and are carried throughout the body. After settling in some organs, the larvae turn into a cysticercus and cause the following symptoms:
- under the skin, multiple or single formations appear, tumor-like, painless, oval-shaped (they are usually localized on the inner side of the shoulders, upper chest and palms);
- in the seals the cavity is felt;
- over time, these seals grow;
- new formations appear;
- when carrying out an educational histology, a cysticercus can be found inside;
- urticaria;
- knots rarely deteriorate, but more often they do not change for many years and occasionally resolve.
Symptoms of Schistosomiasis
Schistosome larvae can penetrate human skin directly from the aquatic environment. Within hours, they can be in the bloodstream. With invasion of the skin, the following symptoms appear:
- urticaria;
- severe itching;
- patchy rashes appear every other day.
Then follows a period of calm for several weeks. In the circulatory system, schistosomes reach the stage of sexually mature individuals and migrate into the vascular system of the genitourinary system. After a couple of months, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- dry cough;
- feverish condition;
- urticaria;
- severe night sweats;
- liver enlargement;
- vaginal bleeding;
- blood in the urine;
- pathology of the prostate, kidneys and bladder;
- knots on the genitals;
- infertility.
Important! In childhood, schistosomiasis contributes to decreased learning ability, anemia, developmental delay, and memory impairment.
Symptoms of dracunculiasis
If a person drinks water containing infected copepods, then after his death, helminth larvae are released into the patient's digestive system. They penetrate the retroperitoneal space and migrate through the lymphatic system into soft tissues. Only after 3 months, the female of this parasite can invade the skin or connective tissues for further development. As the female grows, the patient develops the characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- an allergic reaction to the infection appears only after 10-14 months in the form of hives, fainting, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and suffocation;
- a year later, a rishtosis blister appears on the skin (its diameter reaches 2-7 cm, but there are no signs of inflammation);
- you can see a helminth in the bladder;
- after a few days the bubble itself opens and the necrotic masses are rejected;
- at the autopsy, the patient feels a burning sensation and sharp pains.
It is worth knowing! Rishtose blisters are usually found on the skin of the legs, but can sometimes be found on the stomach, arms, and other parts of the body. In addition, the female can settle in the connective tissues of the joints. In this case, its immobility, contracture and inflammation of the bursa appear.
With a secondary infection, there can be phlegmon, abscesses, sepsis and gangrene. If a patient with an open bladder falls into a tank, thousands of larvae will again be swallowed by the cyclops crustaceans, which will cause the infection to spread further.